Manual Muscle Testing (MMT), a cornerstone of functional assessments, gains prominence within functional medicine for its diagnostic capabilities.
It allows practitioners to evaluate muscle strength and identify imbalances, correlating them with potential underlying health issues.
Online resources offer vast libraries of manuals, aiding in understanding this technique and its applications in holistic healthcare approaches.
What is Manual Muscle Testing (MMT)?
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) is a procedure used to evaluate the strength of individual muscles, or muscle groups, against the resistance applied by the examiner.
It’s a foundational skill in physical and functional medicine, involving palpating a muscle and observing its contractile response.
The process doesn’t just assess raw strength; it reveals neurological integrity and how efficiently the body recruits muscles.
Online manuals and guides detail the specific techniques, emphasizing proper positioning and consistent application of force.
MMT helps identify weaknesses potentially linked to nutritional deficiencies, inflammation, or gut dysfunction – key areas addressed in functional medicine.
Essentially, it’s a hands-on diagnostic tool providing valuable insights into overall physiological function.
The Role of Functional Medicine
Functional Medicine views health as a dynamic interplay between genetics, lifestyle, and environment, seeking root causes of illness rather than merely treating symptoms.
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) seamlessly integrates into this approach, offering a tangible way to assess how various factors impact physiological function.
By identifying muscle weaknesses, practitioners can investigate underlying imbalances – nutritional deficits, inflammation, or gut-related issues.
Online resources, including user manuals, highlight the importance of a holistic assessment.
MMT findings inform personalized interventions, like dietary changes or targeted supplementation, aiming to restore optimal muscle function and overall health.
It’s a crucial tool for uncovering hidden stressors and supporting the body’s innate healing capabilities.
Principles of Manual Muscle Testing
MMT relies on assessing muscle contractions against resistance, evaluating strength and identifying neurological or biomechanical impairments.
Understanding these principles is vital for accurate functional assessments and informed healthcare decisions.
Neuromuscular Junction Assessment
Assessing the neuromuscular junction during Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) is crucial in functional medicine. This junction, where nerves meet muscle fibers, dictates effective muscle contraction. Weakness here can stem from various factors, impacting overall function.
Practitioners observe how quickly and fully a muscle responds to commands. Delayed or incomplete contractions suggest potential issues at this critical interface. Online manuals emphasize the importance of precise technique to differentiate between true weakness and other limitations.
Evaluating this junction helps pinpoint subtle neurological impairments often missed by standard strength tests, guiding targeted interventions for optimal patient outcomes.
Grading Muscle Strength
Grading muscle strength in Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) utilizes a standardized 0-5 scale, providing a quantifiable measure of muscle function. A grade of 0 indicates no contraction, while 5 represents normal strength against maximal resistance.
Functional medicine practitioners rely on this grading to track progress and identify specific weaknesses. Consistent application of this scale, as detailed in numerous online manuals, ensures reliable results.
Accurate grading isn’t merely about force; it considers the quality of contraction and patient effort. This detailed assessment informs personalized treatment plans, addressing underlying imbalances and optimizing movement patterns.
MMT and Functional Assessment
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT), integrated into functional assessments, reveals crucial insights into movement patterns and identifies muscle imbalances impacting overall health.
Identifying Muscle Imbalances
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) excels at pinpointing muscle imbalances – weaknesses in specific muscles or muscle groups – that contribute to dysfunctional movement patterns. These imbalances aren’t isolated issues; they often signal underlying problems within the functional medicine framework.
Through systematic testing, practitioners can determine if a muscle is weak, strong, or exhibiting altered tone. Identifying these discrepancies is vital because imbalances can stem from nutritional deficiencies, inflammation, or even gut-related issues, all central to functional medicine’s holistic approach.
Correcting these imbalances is key to restoring optimal biomechanics and alleviating pain, ultimately improving a patient’s overall well-being. Online manuals and resources can aid in mastering these assessment techniques.
Assessing Movement Patterns
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) extends beyond isolated muscle strength to evaluate how muscles work together during functional movements. This holistic assessment reveals compensations and inefficiencies in movement patterns, offering crucial insights for functional medicine practitioners.
By observing how a patient performs specific movements – like squats or reaching – clinicians can identify limitations and imbalances. These patterns often reflect underlying physiological dysfunction, potentially linked to nutritional deficiencies or inflammatory processes.
Understanding these movement impairments allows for targeted interventions, including dietary adjustments and lifestyle modifications, to restore optimal biomechanics and improve overall functional capacity. Accessing online manuals can refine these assessment skills.
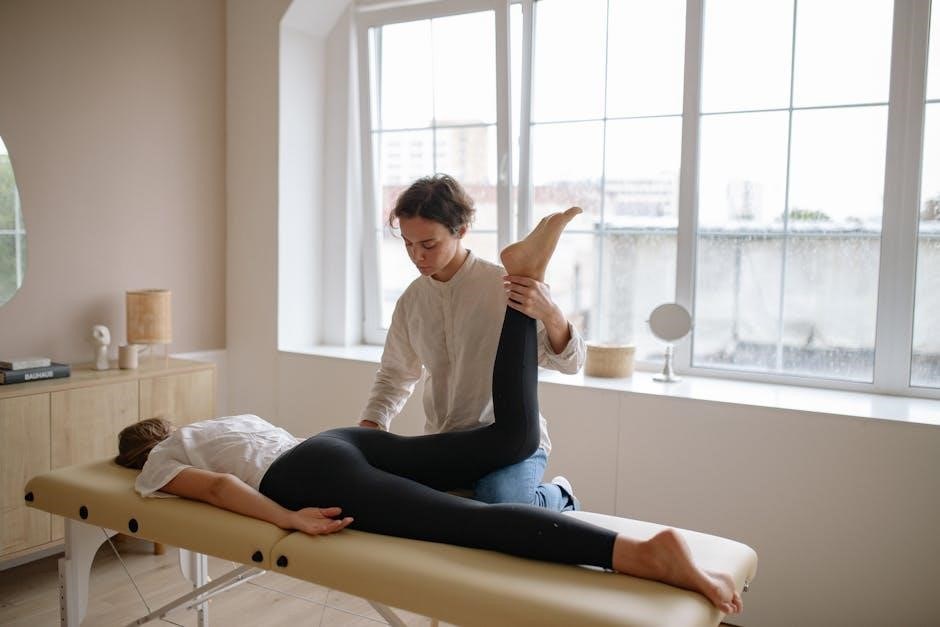

MMT in Identifying Underlying Issues
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) reveals connections between muscle weakness and systemic factors like nutritional deficits, inflammation, and gut health, aiding functional diagnosis.
Nutritional Deficiencies & Muscle Weakness
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) serves as a valuable tool in functional medicine for uncovering links between nutritional status and muscle function. Specific muscle weaknesses identified through MMT can indicate deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals, such as magnesium, potassium, or vitamin D.
For example, consistent weakness in certain muscle groups might suggest a need for targeted nutritional support. Practitioners can correlate MMT findings with laboratory testing to confirm deficiencies and tailor dietary or supplementation plans.
Addressing these nutritional imbalances can then lead to improved muscle strength and overall health outcomes, demonstrating the power of personalized functional medicine approaches.
Impact of Inflammation on Muscle Function
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) in functional medicine reveals how systemic inflammation profoundly impacts muscle performance. Chronic inflammation, often stemming from gut dysbiosis or autoimmune responses, can inhibit muscle fiber recruitment and reduce overall strength.
MMT can pinpoint specific muscle weaknesses that correlate with inflammatory pathways. Practitioners utilize this information to investigate underlying causes of inflammation, employing lab tests to assess inflammatory markers.
Dietary modifications, like reducing processed foods and increasing anti-inflammatory nutrients, alongside lifestyle interventions, can then be implemented to mitigate inflammation and restore optimal muscle function.
The Gut-Muscle Connection
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) highlights the surprising, yet crucial, link between gut health and muscle function within functional medicine. A compromised gut microbiome can lead to nutrient malabsorption, directly impacting muscle protein synthesis and energy production.
MMT can reveal muscle weaknesses that correlate with gut-related imbalances. Identifying these connections allows practitioners to address digestive issues, such as leaky gut or dysbiosis, through targeted dietary changes and supplementation.
Restoring gut health often translates to improved muscle strength and reduced fatigue, demonstrating the powerful interplay between these two systems.
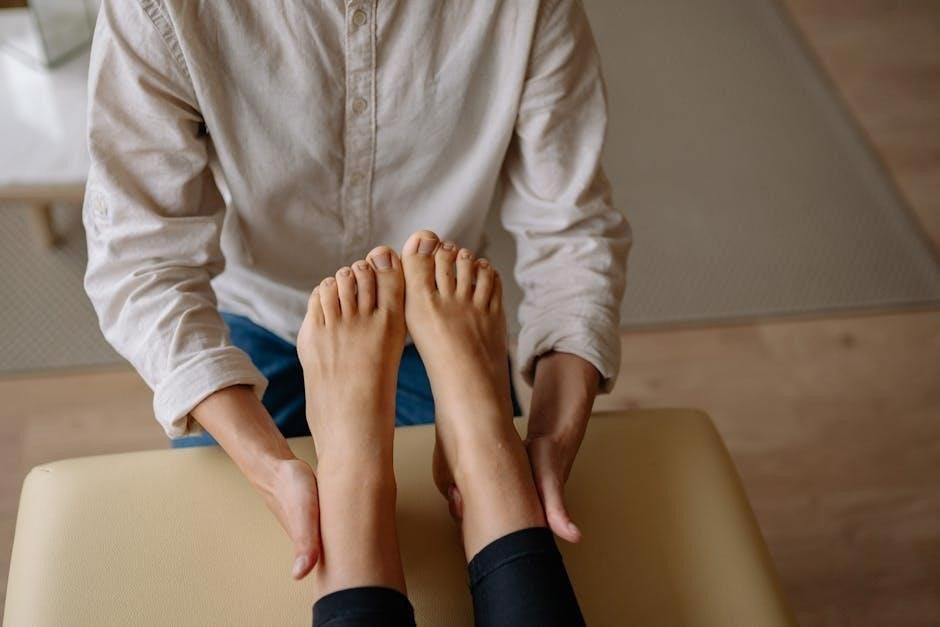

Specific MMT Protocols in Functional Medicine
Functional MMT employs targeted muscle group testing and movement screens to pinpoint weaknesses, revealing systemic imbalances and guiding personalized treatment plans.
Testing Key Muscle Groups
Evaluating core muscles – abdominals, obliques, and lower back – is fundamental, as weakness here impacts overall stability and movement patterns. Shoulder girdle assessment, including deltoids, rotator cuff muscles, and trapezius, reveals postural imbalances and potential nerve impingement.
Hip and leg muscle testing, focusing on gluteals, hamstrings, quadriceps, and adductors, identifies gait abnormalities and structural weaknesses. Practitioners systematically assess these groups, noting strength deviations.
Detailed protocols often involve isolating specific muscles and applying resistance while observing movement quality. Online manuals and resources provide guidance on proper testing techniques, ensuring accurate and reliable results for functional medicine applications.
Functional Movement Screens with MMT
Integrating MMT into functional movement screens provides a dynamic assessment of how the body moves as a whole. Common screens include overhead squats, lunges, and push-ups, observed for compensations and limitations.
MMT is then applied during these movements to pinpoint specific muscle weaknesses contributing to dysfunctional patterns. This reveals not just if a muscle is weak, but when it fails during functional tasks.
Online resources detail standardized screen protocols and MMT integration. This combined approach offers a more comprehensive picture than isolated muscle testing, guiding targeted interventions for optimal functional restoration.
Integrating MMT with Other Functional Medicine Tools
MMT findings correlate with lab results, dietary assessments, and lifestyle factors, creating a holistic patient profile for personalized functional medicine interventions.
Lab Testing Correlation
Correlating MMT results with comprehensive lab testing is crucial in functional medicine. Weakness in specific muscle groups, identified through MMT, can prompt investigation into related nutrient deficiencies – like Vitamin D or magnesium – confirmed via blood analysis.
Inflammatory markers, assessed through lab work, can explain muscle function impairment revealed during testing.
For example, elevated inflammatory cytokines might correlate with reduced strength in certain muscle groups.
Gut health assessments, including stool analysis, can be linked to MMT findings, as gut dysbiosis often impacts nutrient absorption and muscle function.
This integrated approach provides a more complete clinical picture.
Dietary and Lifestyle Modifications Based on MMT Findings
MMT findings directly inform personalized dietary and lifestyle interventions within functional medicine. Identified muscle weaknesses linked to potential nutritional deficits guide targeted supplementation – for instance, addressing low iron with dietary changes or a supplement;
Inflammation-related muscle dysfunction prompts an anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants.
Gut-muscle connection insights lead to dietary adjustments like eliminating food sensitivities or incorporating probiotic-rich foods.
Lifestyle recommendations, including stress management techniques and tailored exercise programs, further support muscle recovery and optimal function.

MMT for Specific Conditions
MMT proves valuable in assessing conditions like fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue, and autoimmune diseases, revealing unique muscle patterns and guiding targeted functional medicine strategies.
Fibromyalgia and MMT
Fibromyalgia often presents with widespread pain and muscle tenderness, making traditional strength assessments challenging. Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) offers a nuanced approach, identifying specific muscle weaknesses that correlate with pain patterns and functional limitations.
Unlike standard tests, MMT in fibromyalgia focuses on subtle changes in muscle firing and endurance, revealing underlying neurological impairments. Practitioners can pinpoint trigger points and assess the impact of inflammation on muscle function.
This information guides personalized functional medicine interventions, including targeted nutritional support, stress management techniques, and gentle exercise protocols, aiming to restore muscle balance and alleviate pain. Online resources can help understand these applications.
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome & Muscle Testing
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) frequently manifests with profound muscle weakness and fatigue, often disproportionate to activity levels. Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) becomes invaluable in discerning the specific muscle groups affected and identifying patterns of weakness that differentiate CFS from other conditions.
MMT can reveal subtle neurological deficits contributing to muscle dysfunction, even when conventional strength tests appear normal. This assessment aids in uncovering underlying factors like mitochondrial dysfunction or adrenal fatigue impacting muscle energy production.
Findings inform personalized functional medicine strategies, including targeted supplementation, dietary adjustments, and restorative therapies, aiming to enhance energy levels and improve muscle function; Online manuals can assist in understanding these protocols.
Autoimmune Disease Assessment
Autoimmune diseases often present with widespread inflammation and fluctuating muscle weakness, making diagnosis challenging. Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) offers a functional assessment tool to identify specific muscle groups compromised by autoimmune activity, even before conventional lab markers become significantly elevated.
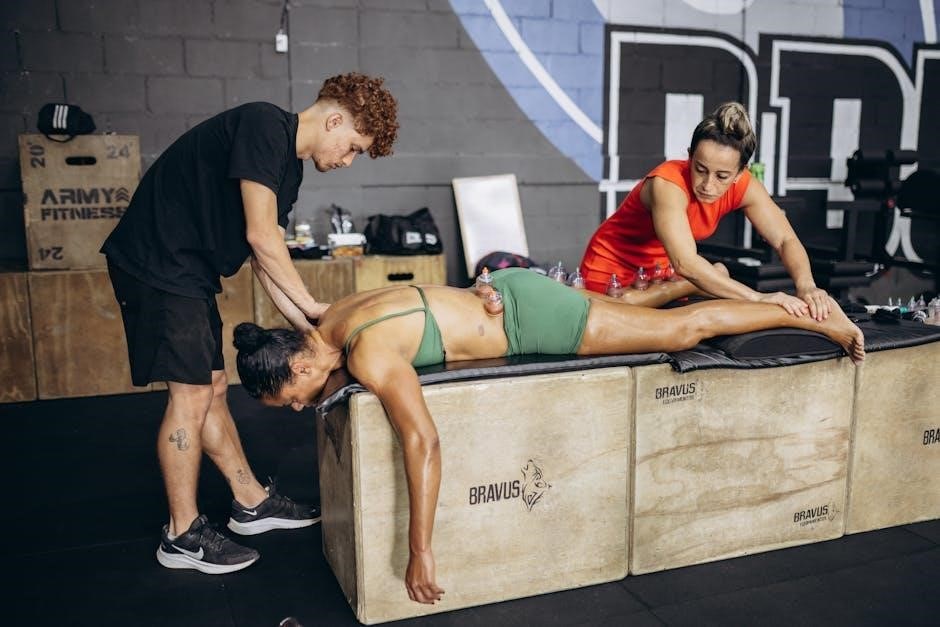

MMT can reveal patterns of weakness correlating with specific autoimmune conditions, aiding in differential diagnosis. It helps assess the impact of inflammation on neuromuscular function and identify potential nutrient deficiencies exacerbating muscle weakness.
Integrating MMT with lab testing and dietary modifications, guided by online resources and manuals, supports a personalized functional medicine approach to manage autoimmune symptoms and improve muscle strength.
Advanced Techniques in MMT
Beyond basic testing, advanced MMT incorporates palpation for tissue texture and dynamic assessments evaluating muscle function during movement patterns.
Palpation and Tissue Texture Assessment
Palpation, a crucial advanced MMT technique, involves carefully feeling the muscle belly to assess its tone, temperature, and texture. Practitioners seek areas of tenderness, tightness, or asymmetry, which can indicate underlying dysfunction or inflammation.

Changes in tissue texture – such as ropey, boggy, or hard areas – provide valuable clues about hydration levels, fascial restrictions, and potential metabolic imbalances. This tactile assessment complements muscle strength testing, offering a more comprehensive understanding of muscle health.
Combined with functional movement screens, palpation helps pinpoint specific areas needing attention, guiding targeted interventions and supporting personalized treatment plans within a functional medicine framework.
Dynamic Muscle Testing
Dynamic Muscle Testing (DMT) extends beyond static MMT by evaluating muscle function during movement patterns. This assesses how well muscles work together to perform functional tasks, revealing subtle weaknesses or compensations not apparent in isolated testing.
DMT mimics real-life activities, observing muscle control, coordination, and endurance throughout a range of motion. Practitioners look for deviations in form, pain, or fatigue, identifying limitations impacting daily function.
Integrating DMT with MMT provides a holistic view of neuromuscular health, informing targeted rehabilitation strategies and lifestyle modifications within a functional medicine approach.
Limitations and Considerations of MMT
MMT’s subjectivity and reliance on examiner skill necessitate thorough training. Accurate interpretation requires understanding potential influences and consistent application of protocols.
Subjectivity in Testing
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT), while valuable, inherently involves a degree of subjectivity. The examiner’s skill, experience, and even fatigue levels can influence the assessment of muscle strength. Consistent application of standardized grading scales is crucial, yet subtle variations in technique can occur.
Factors like patient cooperation, pain levels, and psychological state can also impact results, making it essential to consider the whole clinical picture. Unlike objective measures like dynamometry, MMT relies on the examiner’s tactile and visual assessment, introducing potential for inter-rater variability. Therefore, rigorous training and ongoing calibration are vital for reliable MMT findings.
Importance of Proper Training
Effective Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) demands comprehensive training and a solid understanding of neuromuscular anatomy and physiology. Proper training ensures consistent application of standardized testing procedures, minimizing subjectivity and maximizing reliability. Courses and certifications, readily available online, equip practitioners with the necessary skills to accurately assess muscle strength and identify functional imbalances.
Beyond technique, training emphasizes recognizing compensatory patterns and interpreting MMT findings within the broader context of a patient’s health history. Accessing relevant textbooks and guides, like those found in online manual libraries, further enhances competency and promotes confident, informed clinical decision-making.

Resources for Learning MMT
Numerous certifications and online courses provide in-depth MMT training. Online libraries offer free PDF manuals and service guides for comprehensive learning and skill development.
Relevant Certifications
Several organizations offer certifications specifically focused on manual muscle testing within a functional medicine context; Applied Kinesiology (AK) certifications are highly regarded, providing a robust foundation in muscle testing principles and their clinical application.

The International College of Applied Kinesiology (ICAK) is a leading provider, offering various levels of AK training. Functional Movement Systems (FMS) certification, while not solely focused on MMT, incorporates movement assessments that complement muscle testing findings.
Additionally, courses offered by organizations specializing in neuromuscular therapy and rehabilitation can enhance proficiency. Seeking certifications ensures practitioners receive standardized training and demonstrate competency in performing and interpreting MMT effectively.
Recommended Textbooks and Online Courses
Several resources deepen understanding of manual muscle testing in functional medicine. “Muscle Testing and Functional Medicine” by Dr. David Miller provides a comprehensive overview of techniques and clinical applications. “Applied Kinesiology” by George Goodheart is a foundational text for AK principles.
Online, courses from Udemy and Coursera offer introductory and advanced MMT training. The Functional Movement Institute’s website provides resources related to FMS and movement assessment.
Exploring online libraries of user manuals can supplement learning, offering practical guidance. These resources equip practitioners with the knowledge to effectively integrate MMT into their practice.

The Future of MMT in Functional Medicine
Integration with technology and expanded research will refine MMT’s effectiveness, enhancing diagnostic precision and solidifying its role in personalized functional medicine.
Integration with Technology
The fusion of Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) with technological advancements promises a significant evolution in functional medicine. Digital dynamometers offer objective strength measurements, reducing subjectivity inherent in traditional MMT. Software platforms can record and analyze MMT data, identifying subtle patterns and tracking progress over time.
Furthermore, integrating MMT findings with electronic health records streamlines patient information and facilitates collaborative care. Visual guides and online manuals, readily accessible, support practitioners in mastering techniques. This technological synergy enhances diagnostic accuracy, treatment planning, and ultimately, patient outcomes within a holistic framework;
Expanding Research on MMT Effectiveness
Robust scientific investigation is crucial to solidify the role of Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) within functional medicine. Current research should focus on establishing standardized protocols and quantifying the correlation between MMT findings and specific biochemical imbalances. Studies exploring MMT’s predictive value for treatment response are also essential.
Larger-scale clinical trials are needed to validate MMT’s effectiveness across diverse patient populations and conditions; Access to comprehensive online manuals and resources can aid researchers. Ultimately, rigorous evidence will empower practitioners and enhance the integration of MMT into mainstream healthcare practices.

Leave a Reply